Research
Big Picture
The landscape and word cloud visualization of my research thrusts and PhD thesis:
 |
Here are a number of research projects that I have been working on.
Power System State Estimation
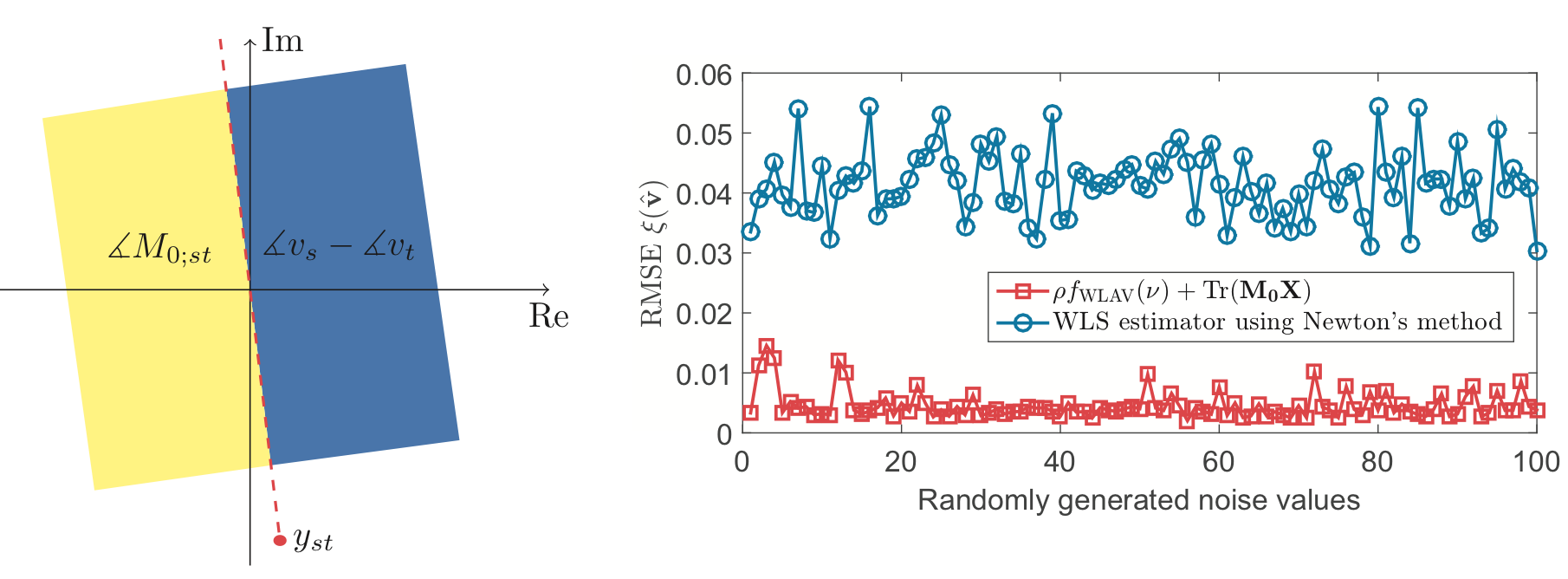 |
Left figure: The acceptable regions for the voltage phase difference (blue open half space), and the entry of coefficient matrix (yellow open half space) are shown relative to the line admittance (red dot). |
Research challenges:
1. How to deal with the non-convex optimization problem formulated for the state estimation?
2. How good is the performance of convexification ?
Contributions:
We propose a convexification framework based on semidefinite programming (SDP)
and second-order cone programming (SOCP) relaxations to cope
with inherent non-convexity of power flow (PF) and power system state estimation (PSSE) problems.
We study the performance of the proposed framework in the case where the set of measurements
includes: (i) nodal voltage magnitudes, and (ii) branch active
power flows over a spanning tree of the network. It is shown that the SDP and SOCP relaxations
both recover the true PF solution as long as the voltage angle difference across each
line of the network is not too large. By capitalizing on the result for the PF problem,
penalized SDP and SOCP problems are designed to solve the PSSE.
Strong theoretical results are derived to quantify the optimal solution of
the penalized SDP problem, which is shown to possess a dominant
rank-one component formed by lifting the true voltage vector.
An upper bound on the estimation error is also derived as a
function of the noise power, which decreases exponentially fast
as the number of measurements increases.
Related paper:
Power System State Estimation with Line Measurements, 2016
Yu Zhang, Ramtin Madani, and Javad Lavaei
Robust and Stochastic Energy Management with High-Penetration Renewables
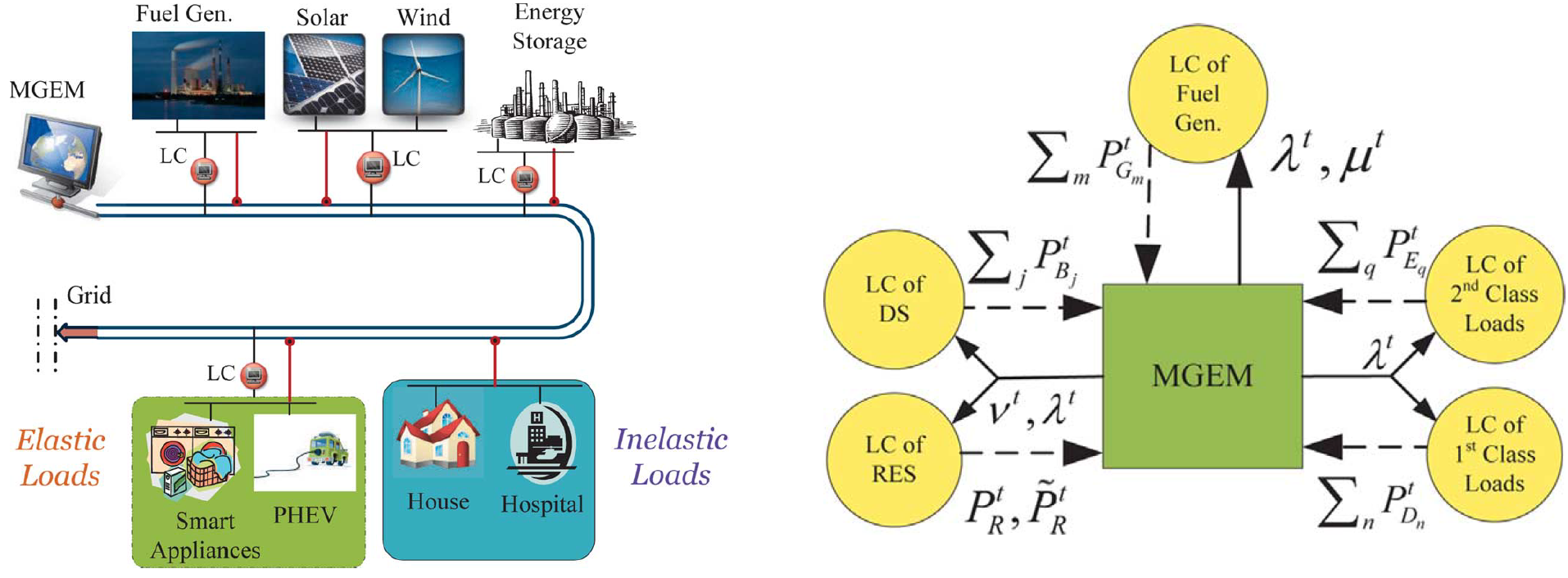 |
Left figure: Typical infrastructure of a microgrid with distributed energy resources. |
Research challenges:
1. How to handle the inherent uncertainty of renewable energy sources for day-ahead market clearing and power dispatch?
2. How to engage all local controllers in the distributed energy management for microgrids?
Contributions: Due to its reduced communication overhead and robustness
to failures, distributed energy management is of paramount
importance in smart grids, especially in microgrids, which
feature distributed generation (DG) and distributed storage (DS).
To address the intrinsically stochastic availability of renewable energy sources
(RES), a novel power scheduling approach is introduced. The approach
involves the actual renewable energy as well as the energy
traded with the main grid, so that the supply–demand balance is
maintained. Leveraging the dual decomposition, the optimization
problem formulated is solved in a distributed fashion by
the local controllers of DG, DS, and dispatchable loads.
Capitalizing on the conditional value-at-risk (CVaR), the novel day-ahead
stochastic market clearing model is able to mitigate the potentially high risk
of the recourse actions to compensate wind forecast errors.
The resulting convex optimization task is tackled via a distribution-free sample average
based approximation to bypass the prohibitively complex high-dimensional integration.
Furthermore, to cope with possibly large-scale dispatchable loads, a
fast distributed solver is developed with guaranteed convergence
using the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM).
Related papers:
Distributed Stochastic Market Clearing with High-Penetration Wind Power, IEEE Trans. on Power Systems, 2016
Yu Zhang and Georgios GiannakisRobust Energy Management for Microgrids With High-Penetration Renewables, IEEE Trans. on Sustainable Energy, 2013
Yu Zhang, Nikolaos Gatsis, and Georgios GiannakisRobust Optimal Power Flow with Wind Integration using Conditional Value-at-Risk, IEEE SmartGridComm, 2013
Yu Zhang and Georgios GiannakisRisk-aware Management of Distributed Energy Resources, Intl. Conf. on Digital Signal Process., 2013
Yu Zhang, Nikolaos Gatsis, Vassilis Kekatos, and Georgios GiannakisRisk-Constrained Energy Management with Multiple Wind Farms, IEEE-PES Innovative Smart Grid Tech., 2013
Yu Zhang, Nikolaos Gatsis, and Georgios Giannakis
Energy Data Analytics
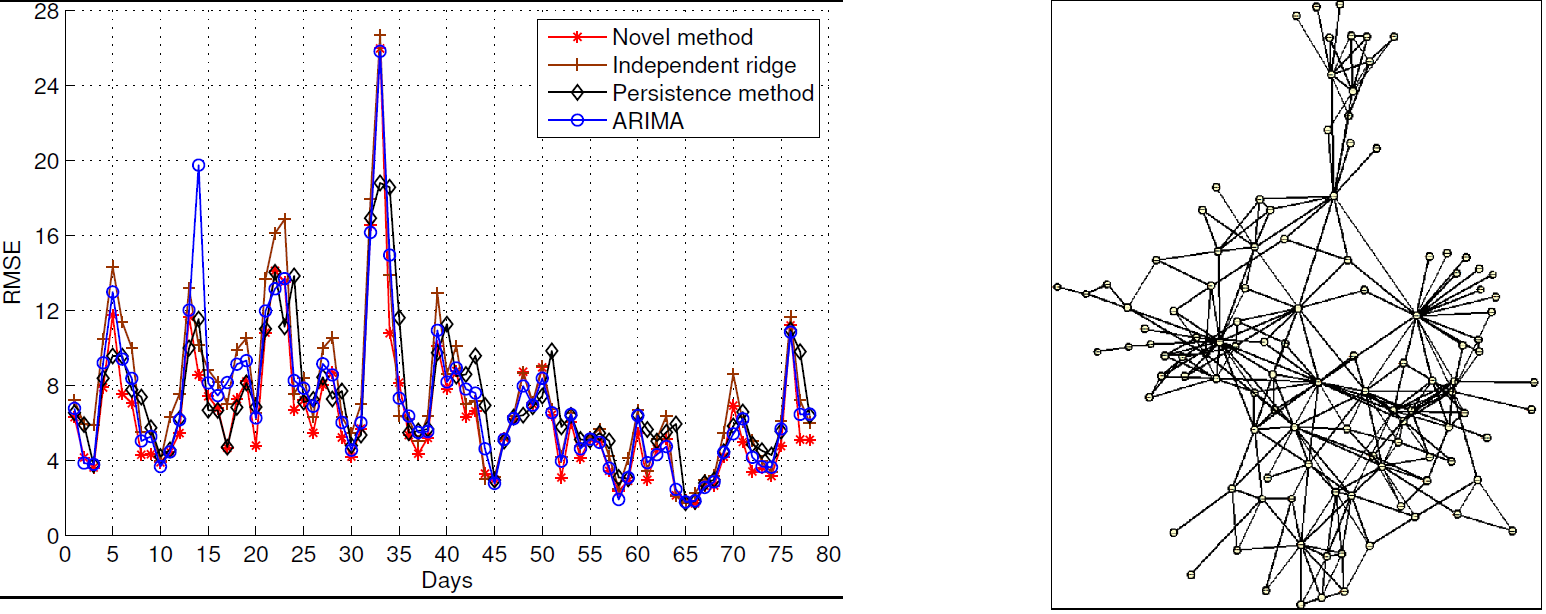 |
Left figure: Root-mean-square error comparison of different forecasting methods. |
Research challenges:
1. How to exploit the valuable spatio-temporal correlations in energy data (electricity prices, load demand, renewable power generation, etc)?
2. How to develop fast and scalable algorithms for massive datasets?
Contributions: The smart grid vision entails advanced information
technology and data analytics to enhance the efficiency, sustainability,
and economics of the power grid infrastructure. Aligned
to this end, modern statistical learning tools are leveraged
for electricity market inference. Day-ahead price forecasting is
cast as a low-rank kernel learning problem. Uniquely exploiting
the market clearing process, congestion patterns are modeled as
rank-one components in the matrix of spatio-temporally varying
prices. Through a novel nuclear norm-based regularization, kernels
across pricing nodes and hours can be systematically selected.
Even though market-wide forecasting is beneficial from a learning
perspective, it involves processing high-dimensional market data.
The latter becomes possible after devising a block-coordinate descent
algorithm for solving the non-convex optimization problem
involved. The algorithm utilizes results from block-sparse vector
recovery and is guaranteed to converge to a stationary point.
Related papers:
Electricity Market Forecasting via Low-Rank Multi-Kernel Learning, IEEE J. of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2014
Vassilis Kekatos, Yu Zhang, and Georgios GiannakisKernel Selection for Power Market Inference via Block Successive Upper Bound Minimization, ICASSP, 2014
Vassilis Kekatos, Yu Zhang, and Georgios GiannakisShort-Term Wind Power Forecasting using Nonnegative Sparse Coding, Conf. on Information Systems and Sciences, 2015
Yu Zhang, Seung-Jun Kim, and Georgios Giannakis
Big Data Sketching
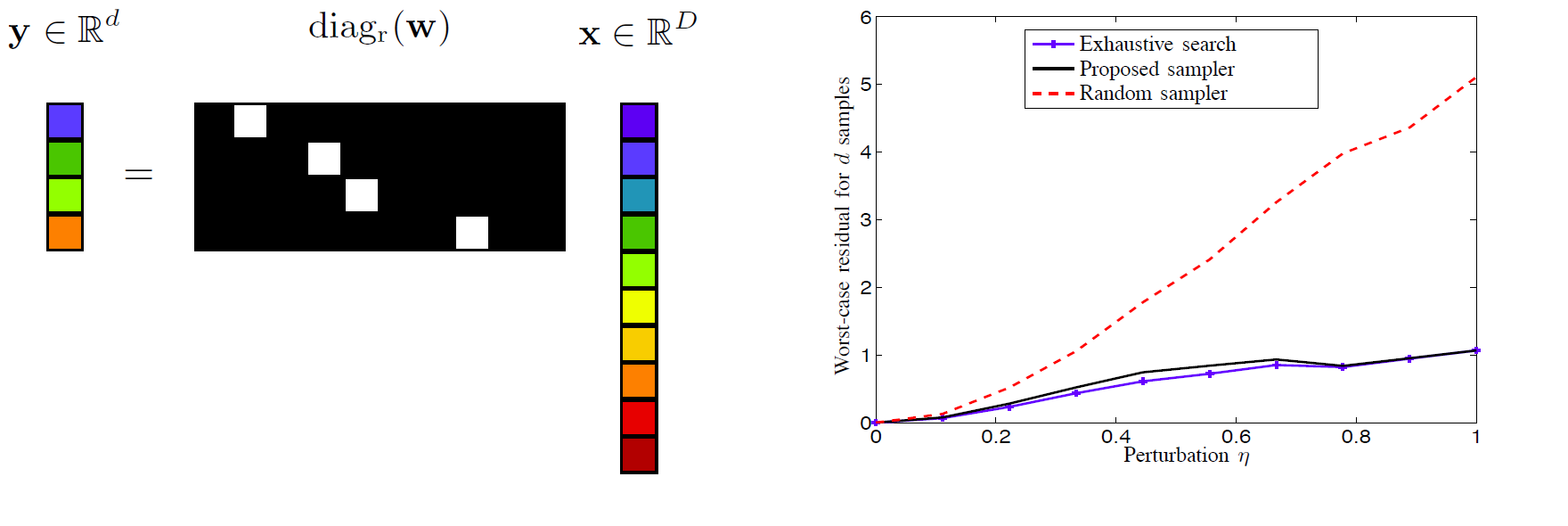 |
Left figure: Sparse sketching scheme for data reduction: A white (black) and colored square represents a one (zero)
and an arbitrary value, respectively. |
Research challenges:
1. How to design efficient samplers for big data sketching robust to model uncertainties?
Abstract: Data reduction for large-scale linear regression is
one of the most important tasks in this era of data deluge.
Exact model information is however not often available for big
data analytics. We propose a framework for big data
sketching (i.e., a data reduction tool) that is robust to possible
model mismatch. Such a sketching task is cast as a Boolean
min-max optimization problem, and then equivalently reduced
to a Boolean minimization program. Capitalizing on the block
coordinate descent algorithm, a scalable solver is developed to
yield an efficient sampler and a good estimate of the unknown
regression coefficient.
Related paper:
Big Data Sketching with Model Mismatch, Asilomar Conf. on Signals, Systems, and Computers, 2015
Sundeep Chepuri, Yu Zhang, Geert Leus, and Georgios Giannakis
Optimal Resource Allocation for Green Communications and Geo-Distributed Data Centers
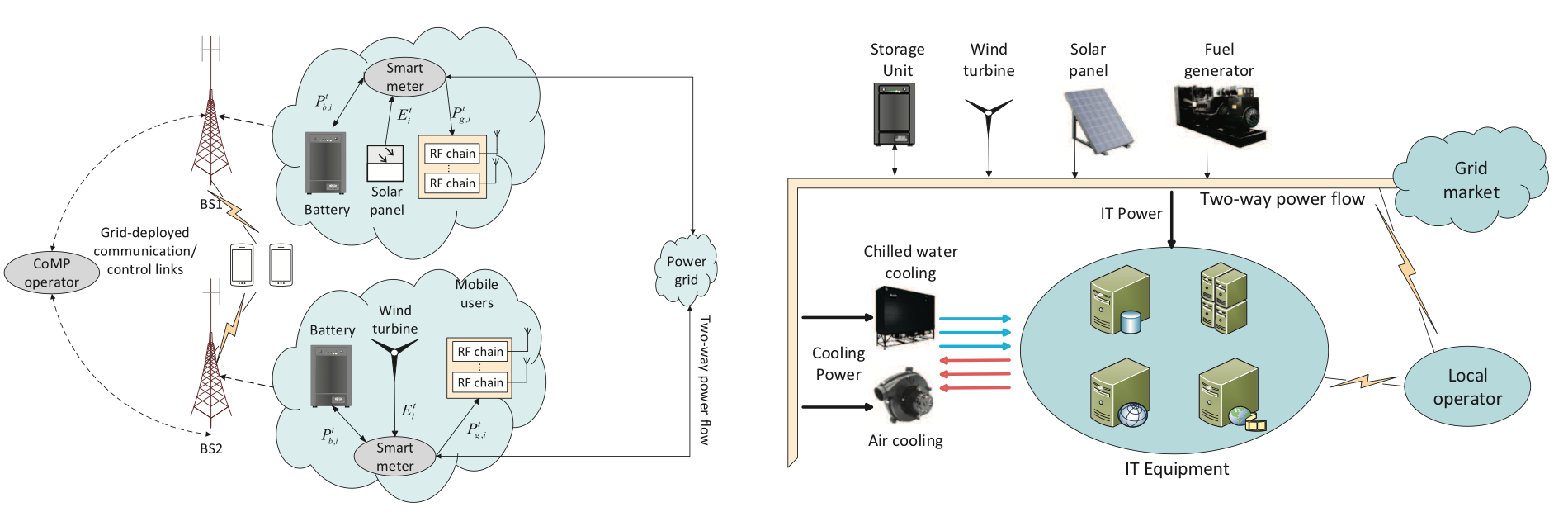 |
Left figure: A smart-grid-powered coordinated multi-point system. |
Research challenges:
1. How to systematically incorporate clean energy sources to support the green and sustainable operations of wireless communication systems and geo-distributed data centers?
2. What is the impact of uncertainties of renewable energy on the ahead-of-time and real-time decision making?
Contributions: We develop dynamic energy management for smart-grid powered coordinated
multi-point (CoMP) transmissions. To address the intrinsic variability
of renewable energy sources, a novel energy transaction
mechanism is introduced for grid-connected base stations that are
also equipped with an energy storage unit. Aiming to minimize
the expected energy transaction cost while guaranteeing the
worst-case users’ quality of service, an infinite-horizon optimization
problem is formulated to obtain the optimal downlink
transmit beamformers that are robust to channel uncertainties.
Capitalizing on the virtual-queue based relaxation technique
and the stochastic dual-subgradient method, an efficient online
algorithm is developed yielding a feasible and asymptotically
optimal solution.
A large number of geo-distributed data centers begin
to surge in the era of data deluge and information explosion.
To meet the growing demand in massive data processing, the
infrastructure of future data centers must be energy-efficient and
sustainable. Facing this challenge, a systematic framework is put
forth to integrate renewable energy sources (RES),
distributed storage units, cooling facilities, as well as dynamic
pricing into the workload and energy management tasks of a
data center network. To cope with RES uncertainty, the resource
allocation task is formulated as a robust optimization problem
minimizing the worst-case net cost.
Related papers:
Dynamic Energy Management for Smart-Grid Powered Coordinated Multipoint Systems, IEEE J. on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016
Xin Wang, Yu Zhang, Tianyi Chen, and Georgios GiannakisRobust Workload and Energy Management for Sustainable Data Centers, IEEE J. on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016
Tianyi Chen, Yu Zhang, Xin Wang, and Georgios GiannakisWeighted Sum-Rate Maximization for MIMO Downlink Systems Powered by Renewables, IEEE Trans. on Wireless Communications, 2016
Shuyan Hu, Yu Zhang, Xin Wang, and Georgios GiannakisRobust Smart-Grid Powered Cooperative Multipoint Systems, IEEE Trans. on Wireless Communications, 2015
Xin Wang, Yu Zhang, Georgios Giannakis, and Shuyan Hu
Optimal Transceiver Design for Wireless Communication Networks
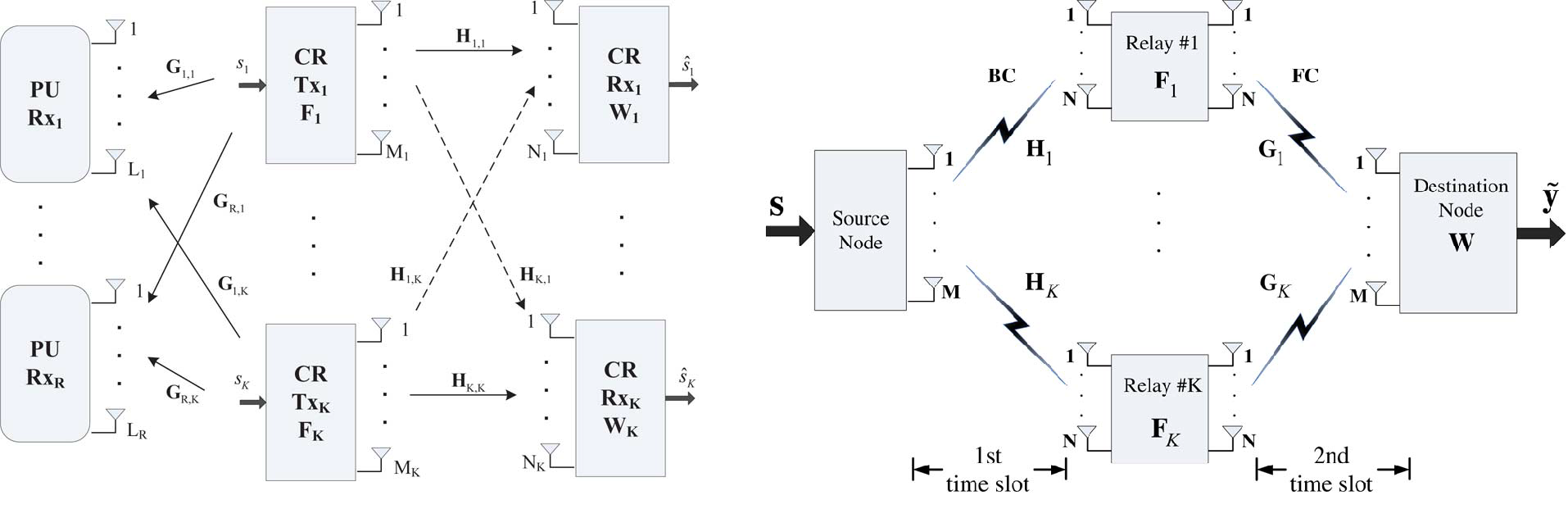 |
Left figure: System model for multi-input multi-output (MIMO) ad-hoc cognitive radio networks. |
Research challenges:
1. How to improve the spectrum efficiency and transmission reliability for cognitive radio systems?
2. How to systematically reduce channel interference to guarantee the end-users’ quality of service?
3. How to simultaneously achieve the distributed array and intra-node array gains for a relay network?
Abstract: We optimize the design of transmit- and receive-beamformers for
ad hoc CR networks when CR-to-CR channels are known, but CR-to-PU channels cannot be estimated accurately.
Capitalizing on a norm-bounded channel uncertainty model, the optimal beamforming
design is formulated to minimize the overall mean-square
error (MSE) from all data streams, while enforcing protection
of the PU system when the CR-to-PU channels are uncertain.
Even though the resultant optimization problem is non-convex,
algorithms with provable convergence to stationary points are
developed by resorting to block coordinate ascent iterations,
along with suitable convex approximation techniques. Enticingly,
the novel schemes also lend themselves naturally to distributed
implementations.
Related papers:
Distributed Optimal Beamformers for Cognitive Radios Robust to Channel Uncertainties, IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2012
Yu Zhang, Emiliano Dall'Anese, and Georgios GiannakisEfficient Relay Beamforming Design With SIC Detection for Dual-Hop MIMO Relay Networks, IEEE Trans. on Vehicular Technology, 2010
Yu Zhang, Hanwen Luo, and Wen Chen